=
Search

Electric system
|
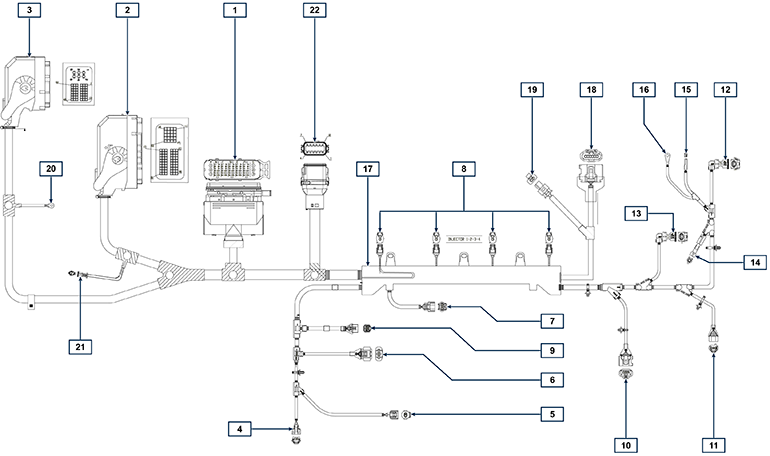
2.13.1 ECU input and output signals diagram
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
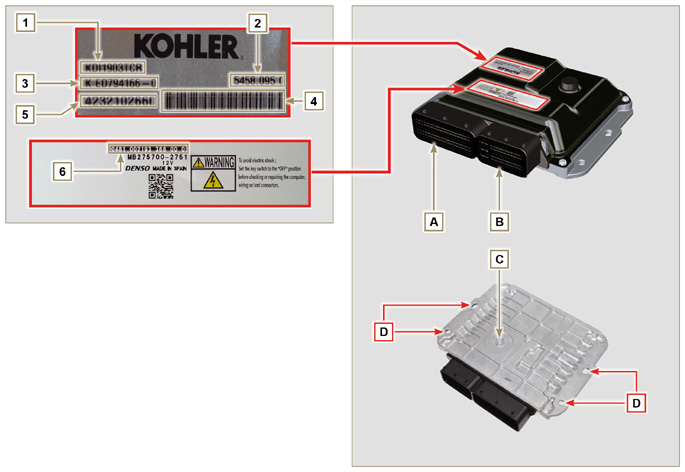
2.13.2 Control unit (ECU)
 Important Important
|
2.13.2.1 Technical features
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Fig 2.32 - Fig 2.33
Tab. 2.35
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
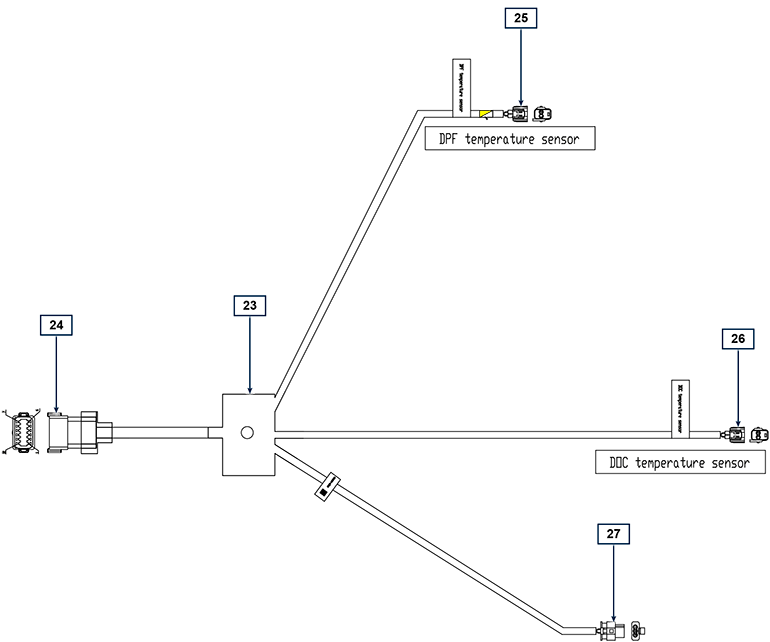
2.13.3 Engine electrical wiring
Fig 2.34 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Tab. 2.36
|
 Fig 2.34a 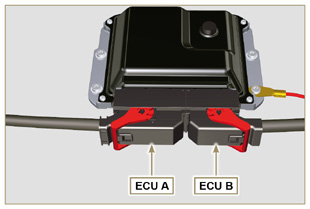 Fig 2.34b |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NOTE: Click by side to play the procedure. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2.13.3.1 Wiring disconnection All sensor connectors and electronic control devices are sealed. The connectors must be disconnected by means of pressure on tabs A or unblock the retainers B, as illustrated from Fig. 2.34c to Fig. 2.34r. |
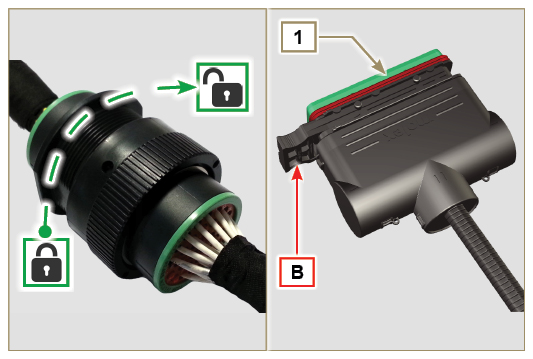 Fig 2.34c |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
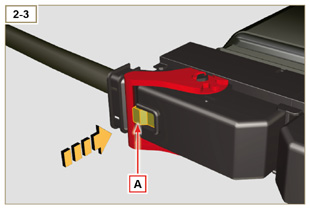 Fig 2.34d |
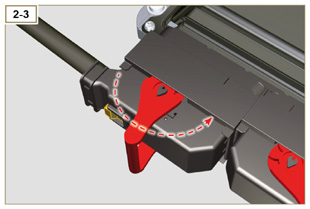 Fig 2.34e |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Fig 2.34f |
 Fig 2.34g |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Fig 2.34h |
 Fig 2.34i |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Fig 2.34l |
 Fig 2.34m |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Fig 2.34n |
 Fig 2.34o |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Fig 2.34p |
 Fig 2.34q |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Fig 2.34r |



 Loading
Loading