=
Search
1
General information

2
Technical information

Important The engine may be damaged if operated with improper oil level. Do not exceed the MAX level because a sudden increase in engine rpm could be caused by its combustion. Use only the recommended oil to ensure adequate protection, efficiency and service life of the engine. The use of lubricants other than recommended may shorten the engine life. Viscosity must be appropriate to the ambient temperature to which the engine is to be exposed. Danger Prolonged skin contact with the exhausted engine oil can cause cancer of the skin. If contact with oil cannot be avoided, thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water as soon as possible. For the exhausted oil disposal, refer to the Par. DISPOSAL and SCRAPPING. 2.4.1 SAE oil classification In the SAE classification, oils are identified according to viscosity without considering any other qualitative characteristic. The code is composed of two numbers, which indicate, and must correspond to, the ambient temperature in which the engine operates, the first number refers to the viscosity when cold, for use during winter ("W"), while the second number is for viscosity at high temperatures. Use oil viscosity based on the experienced air temperature range during the period between oil changes as indicated in the table below. Kohler / Rehlko X-treme 10W-40 formula pro; X-treme 10W-40; X-treme 5W-40 oil are preferred: Oils meeting the following specifications are also recommended. 2.2 RECCOMENDED OIL VISCOSITY SAE 10w-30 (-25°C ÷ +40°C)10w-40 (-25°C ÷ +50°C)5w-30 (-30°C ÷ +40°C)0w-40 (-40°C ÷ +50°C) WITH SPECIFICATIONS API CI-4 PlusCI-4CH-4 ACEA E7 E5 Low S.A.P.S. oils, sulfate ashes <1% may not be used with fuels with a sulfur content >50ppm. Filtration of oils is critical to proper operation and lubrication; always change filters regularly as specified in this manual.
Battery not supplied by Kohler Tab. 2.7 RECOMMENDED BATTERIES AMBIENT TEMPERATURE BATTERY TYPE > - 15°C 12V 100 Ah - 800 CCA/SAE -15°C ÷ -25°C 12V 110 Ah - 950 CCA/SAE < - 25°C 12V 120 Ah - 1000 CCA/SAE
2.9.1 Supply system Important The high pressure supply injection system is highly susceptible to damage if the fuel is contaminated. It is crucial that all components of the injection circuit are thoroughly cleaned before the components are removed. Thoroughly wash and clean the engine before maintenance. Contamination in the fuel supply injection system may cause a reduction in effectiveness / operation of engine fault indication. If the engine is cleaned with high pressure washer, then the nozzle must be kept at a minimum distance of 200mm from the surface, and not directed at electrical components and connectors. The fuel supply system is under low pressure from the tank 1 to the high-pressure fuel injection pump 5. NOTE: The representation of fuel tank is purely indicative. Component not necessarily supplied by KOHLER. Tab 2.12 POS. DESCRIPTION 1 Fuel tank 2 Fuel supply hose from the tank to the injection pump 3 Fuel filter 4 Electrical fuel feed pump 5 Injection pump 6 Injector high-pressure hose from the injection pump to the injectors 7 Injectors Fig 2.4 2.9.2 Fuel return circuit The fuel return circuit is under low pressure. NOTE: The representation of fuel tank is purely indicative. Component not necessarily supplied by KOHLER. Tab 2.13 POS. DESCRIPTION 1 Injectors 2 Injectors fuel return pipe 3 Injection pump 4 Fuel tank 5 Fuel return pipe to the tank Fig 2.5 2.9.3 Injection pump Pressure into the injection pump must be positive in all operating conditions.The injection pump is operated by means of the pump control gear and sends high-pressure fuel to the injectors. NOTE: In the event of leakage from the high pressure circuit do not intervene with the engine running, but turn it off and wait 5 - 10 minutes before checking the leak. Tab 2.14 POS. COMPONENTS DESCRIPTION 1 Accelerator lever 2 Min Adjustment 3 Max Adjustment 4 Torque adjustment 5 High pressure delivery to injectors 6 Return to fuel tank 7 Inlet suction fuel 8 Cold starting device 9 Gasket 10 Shaft 11 Advance settings (locked) 12 Pump identification label 13 Air bleeding screw 14 Pump control shaft blocking device. Fig 2.6 Fig 2.7 2.9.4 Injector It is a device used to introduce fuel, in the form of one or more jets that are adequately pulverised and suitably oriented directly into the combustion chamber. They consist of a metallic body that internally provides a mobile element that acts on the needle: this, rising against the action of a calibrated spring,allows the release of fuel under high pressure. Opening pressure: 260-268 bar (3770-3886 PSI) Important The injectors are calibrated individually. Fuel contamination causes serious damage to the injection system. Tab 2.15 POS. COMPONENTS DESCRIPTION 1 Inlet fuel 2 Gasket 3 Gasket 4 Nozzle 5 Hole for fuel return to fuel tank Fig 2.8 2.9.5 Fuel filter The fuel filter is situated on the crankcase of the engine or it may be assembled on the frame of the vehicle. Tab 2.16 POS. COMPONENTS DESCRIPTION 1 Fuel filter support cartridge 2 Air bleeding screw 3 Cartridge 4 Water in fuel sensor 5 Hole water drainage Tab 2.17 Cartridge characteristics DESCRIPTION VALUE Filtering surface 2.300 cm2 Degree of filtration 5 µm Max operating pressure 2.0 Bar Fig 2.9 2.9.6 Electric fuel pump (optional) When the electric fuel pump is installed in a diesel engine, one must: Remove any filters installed on the inlet of the electric fuel pump; Insert a pre-filter between the tank and the electric pump; The electric pump must be installed on the application at a height from the minimum tank level such as to generate a MAX. pressure drop equal to a column of 500 mm of fuel; Insert a shut-off valve to prevent dry operation due to the emptying of the intake manifold; The electric pump must guarantee a supply pressure at the inlet positive in all conditions. Tab 2.18 POS. DESCRIPTION 1 Fuel tank 2 Arrival pipe from the tank 3 Prefilter 4 Flow pipe from pre-filter to electric pump 5 Electric pump 6 Flow pipe to the fuel filter 7 Fuel filter Fig 2.10 2.9.7 Guards for fuel injection circuit components High-pressure injection circuit components are particularly sensitive to impurities.To prevent impurities, even microscopic ones, from accessing the fuel input or output unions, you are required to close these accesses by means of specific caps as soon as the various tubes are disassembled and disconnected. Disassembly of any component of the injection circuit must not occur in dusty environments. Cap guards must remain closed in their housing (ST_40) until the moment they are to be used. Pay special attention when using the caps and avoid any contamination of dust or dirt of any kind. Even after using the caps illustrated in this paragraph, all components of the injection circuit must be placed with care in environments that are free of any type of impurity. Fig. 2.11 and 2.12 illustrate the caps that must be used on components of the injection circuit. Cap guards must be accurately washed after use and placed back in their housing (ST_40). Important It is highly recommended to have this page visible during disassembly operations of the components of the fuel injection circuit. Fig 2.11 Fig 2.12
3
Safety information

4
Storage information

5
Information regarding discharge of liquids

6
Information for replacing the functional units

7
Information for disassembly

8
Information about overhauling

9
Assembly information

10
Fluids filling information

11
Information about optional components

12
Information on adjustments

13
Tools information

14
Information about failures

15
Glossary


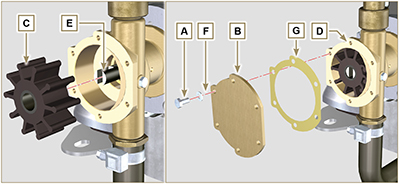
External water pump impeller replacement
|
6.2.1 Disassembly
|
Fig. 6.30 |
|
6.2.2 Assembly
|
Fig. 6.31 |


 Important
Important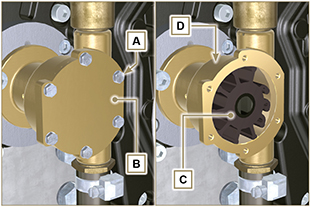
 Loading
Loading